With all the media focus aimed at Greece, we might be inclined to overlook – deliberately or not – that it is merely one case study, and a very small one at that, of what ails the entire world. The whole globe, and just about all of its 200+ nations, is drowning in debt, and more so every as single day passes. Not only is this process not being halted, it gets progressively, if not exponentially, worse. There are differences between countries in depth, in percentages and other details, but at this point these seem to serve mostly to draw attention away from the ghastly reality. ‘Look at so and so, he’s doing even worse than we are!’
Still, though there are plenty accounting tricks available, you’d be hard put to find even one single nation of any importance that could conceivably ever pay back the debt it’s drowning in. That’s why we’re seeing the global currency war slash race to the bottom of interest rates.
Greece is a prominent example, though, simply because it’s been set up as a test case for how far the world’s leading politicians, central bankers, bankers as well as the wizards behind the various curtains are prepared to go. And that does not bode well for you either, wherever you live. Greece is a test case: ho far can we go?
And I’ve made the comparison before, this is what Naomi Klein describes happened in South America, as perpetrated by the Chicago School and the CIA, in her bestseller Shock Doctrine. We’re watching the experiment, we know the history, and we still sit our asses down on our couches? Doesn’t that simply mean that we get what we deserve?
Here’s McKinsey’s debt report today via Simon Kennedy at Bloomberg:
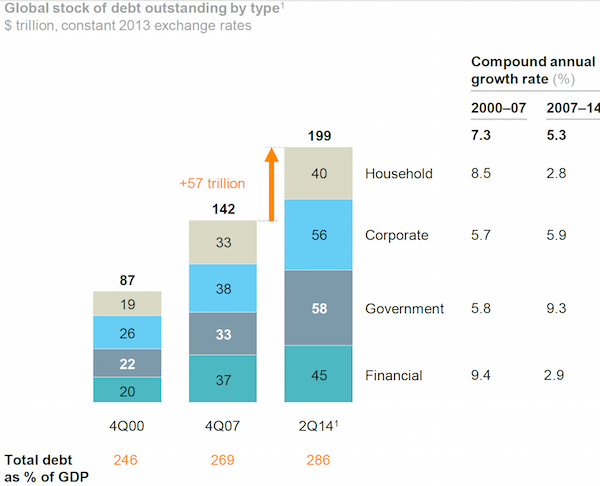
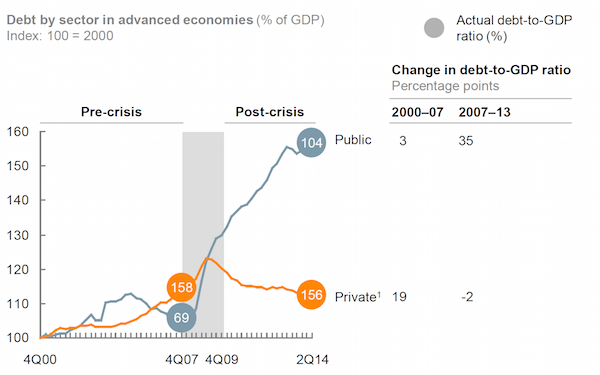
The world economy is still built on debt. That’s the warning today from McKinsey’s research division which estimates that since 2007, the IOUs of governments, companies, households and financial firms in 47 countries has grown by $57 trillion to $199 trillion, a rise equivalent to 17 percentage points of gross domestic product.
While not as big a gain as the 23 point surge in debt witnessed in the seven years before the financial crisis, the new data make a mockery of the hope that the turmoil and subsequent global recession would put the globe on a more sustainable path. Government debt alone has swelled by $25 trillion over the past seven years and developing economies are responsible for almost half of the overall gain. McKinsey sees little reason to think the trajectory of rising leverage will change any time soon. Here are three areas of particular concern:
1. Debt is too high for either austerity or growth to cure. Politicians will instead need to consider more unorthodox measures such as asset sales, one-off tax hikes and perhaps debt restructuring programs.
2. Households in some nations are still boosting debts. 80% of households have a higher debt than in 2007 including some in northern Europe as well as Canada and Australia.
3. China’s debt is rising rapidly. Thanks to real estate and shadow banking, debt in the world’s second-largest economy has quadrupled from $7 trillion in 2007 to $28 trillion in the middle of last year. At 282% of GDP, the debt burden is now larger than that of the U.S. or Germany. Especially worrisome to McKinsey is that half the loans are linked to the cooling property sector.
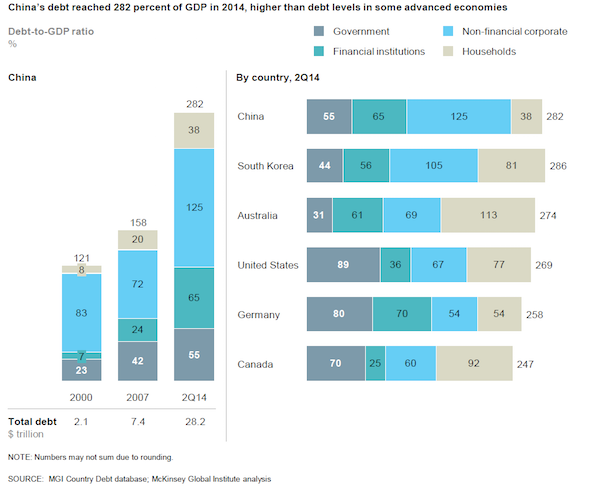
Note: Chinese total debt rose $20.8 trillion in 7 years, or 281%. And we’re talking about Greece as a problem?! You’d think – make that swear – that perhaps Merkel and her ilk have bigger fish to fry. But maybe they just don’t get it?!
Ambrose has this earlier today, just let the numbers sink in:
Devaluation By China Is The Next Great Risk For A Deflationary World
China is trapped. The Communist authorities have discovered, like the Japanese in the early 1990s and the US in the inter-war years, that they cannot deflate a credit bubble safely. A year of tight money from the People’s Bank and a $250bn crackdown on shadow banking have pushed the Chinese economy close to a debt-deflation crisis. Wednesday’s surprise cut in the Reserve Requirement Ratio (RRR) – the main policy tool – comes in the nick of time. Factory gate deflation has reached -3.3%.
The official gauge of manufacturing fell below the “boom-bust” line to 49.8 in January. Haibin Zhu, from JP Morgan, says the 50-point cut in the RRR from 20% to 19.5% injects roughly $100bn into the system. This will not, in itself, change anything. The average one-year borrowing cost for Chinese companies has risen from zero to 5% in real terms over the past three years as a result of falling inflation.
UBS said the debt-servicing burden for these firms has doubled from 7.5% to 15% of GDP. Yet the cut marks an inflection point. There will undoubtedly be a long series of cuts before China sweats out its hangover from a $26 trillion credit boom. Debt has risen from 100% to 250% of GDP in eight years. By comparison, Japan’s credit growth in the cycle preceding its Lost Decade was 50% of GDP.
Wednesday’s trigger was an amber warning sign in the jobs market. The employment component of the manufacturing survey contracted for the 15th month. Premier Li Keqiang targets jobs – not growth – and the labour market is looking faintly ominous for the first time. Unemployment is supposed to be 4.1%, a make-believe figure. A joint study by the IMF and the International Labour Federation said it is really 6.3% [..]
Whether or not you call it a hard-landing, China is struggling. Home prices fell 4.3% in December. New floor space started has slumped 30% on a three-month basis. This packs a macro-economic punch. A study by Jun Nie and Guangye Cao for the US Federal Reserve said that since 1998 property investment in China has risen from 4% to 15% of GDP, the same level as in Spain at the peak of the “burbuja”. The inventory overhang has risen to 18 months compared with 5.8 in the US.
The property slump is turning into a fiscal squeeze since land sales make up 25% of local government money. Zhiwei Zhang, from Deutsche Bank, says land revenues crashed 21% in the fourth quarter of last year. “The decline of fiscal revenue is the top risk in China and will lead to a sharp slowdown,” he said.
Asia is already in a currency cauldron, eerily like the onset of the 1998 crisis. The Japanese yen has fallen by half against the Chinese yuan since Abenomics burst upon the Pacific Rim. Japanese exporters pocketed the windfall gains of devaluation at first to boost margins. Now they are cutting prices to gain export share, exporting deflation.
This is eroding the wafer-thin profit margins of Chinese companies and tightening monetary conditions into the downturn. David Woo, from Bank of America, says Beijing may be forced to join the currency wars to defend itself, even though this variant of the “Prisoner’s Dilemma” leaves everybody worse off. “We view a meaningful yuan devaluation as a major tail-risk for the global economy,” he said.
If this were to happen, it would send a deflationary impulse worldwide. China spent $5 trillion on fixed investment last year, more than Europe and America combined, increasing its overcapacity in everything from shipping to steels, chemicals and solar panels , to even more unmanageable levels. A yuan devaluation would dump this on everybody else. Such a shock would be extremely hard to combat. Interest rates are already zero across the developed world. Five-year bond yields are negative in six European countries. The 10-year Bund has dropped to 0.31. These are no longer just 14th century lows. They are unprecedented.
[..] .. helicopter money, or “fiscal dominance”, may be dangerous, but not nearly as dangerous as the alternative. China faces a Morton’s Fork. Li Keqiang has been trying for two years to tame the state’s industrial behemoths, and trying to wean the economy off credit. Yet virtuous intent has run into cold reality. It cannot be done. China passed the point of no return five years ago.
That ain’t nothing to laugh at. But still, Malcolm Scott has more for Bloomberg:
Pushing on a String? Two Charts Showing China’s Dilemma
Is China’s latest monetary easing really going to help? While economists see it freeing up about 600 billion yuan ($96 billion), that assumes businesses and consumers want to borrow. This chart may put some champagne corks back in. It shows demand for credit is waning even as money supply continues its steady climb.
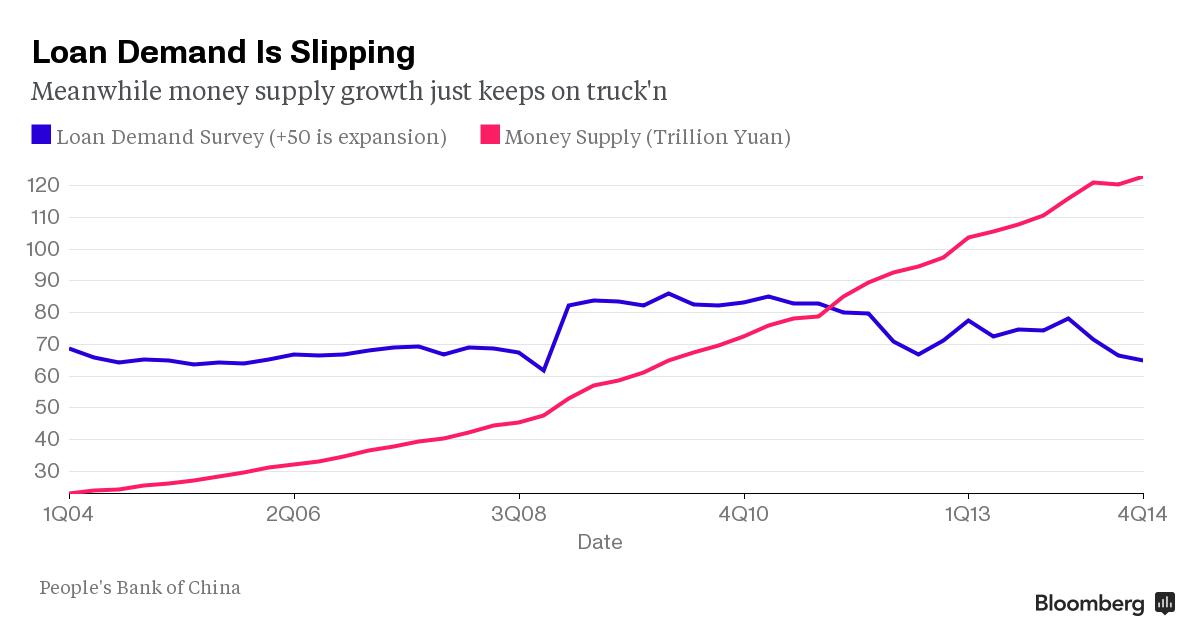
The reserve ratio requirement cut “helps to raise loan supply, but loan demand may remain weak,” said Zhang Zhiwei, chief China economist at Deutsche Bank. “We think the impact on the real economy is positive, but it is not enough to stabilize the economy.” This chart may also give pause. It shows the surge in debt since 2008, which has corresponded with a slowdown in economic growth.
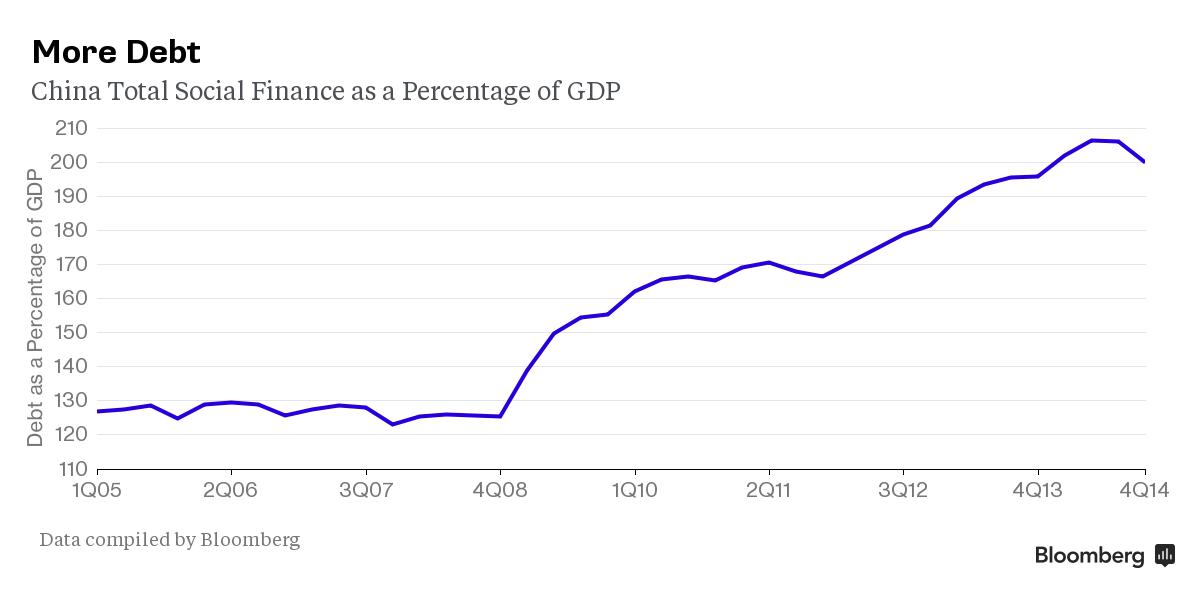
Note: Social finance is, to an extent, just another word for shadow banking.
“Monetary stimulus of the real economy has not worked for several years,” said Derek Scissors, a scholar at the American Enterprises Institute in Washington who focuses on Asia economics. “The obsession with monetary policy is a problem around the world, but only China has a money supply of $20 trillion.”
China now carries $28 trillion in debt, or 282% of its GDP, $20 trillion of which was added in just the past 7 years. It’s also useful to note that it boosted its money supply to $20 trillion. What part of these numbers includes shadow banking, we don’t know – even if social finance can be assumed to include an X amount of shadow funding-. However, there can be no doubt that China’s real debt burden would be significantly higher if and when ‘shadow debt’ would be added.
Ergo: whether it’s tiny Greece, or behemoth China, or any given nation in between, they’re all in debt way over their heads. One might be tempted to ponder that debt restructuring would be worth considering. A first step towards that would be to look at who owes what to whom. And, of course, who profits. When it comes to Greece, that’s awfully clear, something you may want to consider next time you think about who’s squeezing who. From the Jubilee Debt Campaign through Telesur:

That doesn’t leave too many questions, does it? As in, who rules this blue planet?! That also tells you why there won’t be any debt restructuring, even though that is exactly what this conundrum calls for. Debt is a power tool. Debt is how the Roman Empire managed to stretch its existence for many years, as it increasingly squeezed the periphery. And then it died anyway. Joe Stiglitz gives it another try, and in the process takes us back to Greece:
A Greek Morality Tale: We Need A Global Debt Restructuring Framework
At the international level, we have not yet created an orderly process for giving countries a fresh start. Since even before the 2008 crisis, the UN, with the support of almost all of the developing and emerging countries, has been seeking to create such a framework. But the US is adamantly opposed; perhaps it wants to reinstitute debtor prisons for over indebted countries’ officials (if so, space may be opening up at Guantánamo Bay).
The idea of bringing back debtors’ prisons may seem far-fetched, but it resonates with current talk of moral hazard and accountability. There is a fear that if Greece is allowed to restructure its debt, it will simply get itself into trouble again, as will others. This is sheer nonsense. Does anyone in their right mind think that any country would willingly put itself through what Greece has gone through, just to get a free ride from its creditors?
If there is a moral hazard, it is on the part of the lenders – especially in the private sector – who have been bailed out repeatedly. If Europe has allowed these debts to move from the private sector to the public sector – a well-established pattern over the past half-century – it is Europe, not Greece, that should bear the consequences. Indeed, Greece’s current plight, including the massive run-up in the debt ratio, is largely the fault of the misguided troika programs foisted on it. So it is not debt restructuring, but its absence, that is “immoral”. </B.\>
There is nothing particularly special about the dilemmas that Greece faces today; many countries have been in the same position. What makes Greece’s problems more difficult to address is the structure of the eurozone: monetary union implies that member states cannot devalue their way out of trouble, yet the modicum of European solidarity that must accompany this loss of policy flexibility simply is not there.
You can put it down to technical or structural issues, but down the line none of that will convince me. Who cares about talking about technical shit when people are suffering, without access to doctors, and/or dying, in a first world nation like Greece, just so Angela Merkel and Mario Draghi and Jeroen Dijsselbloem can get their way?
Oh, no, wait, that graph there says it’s not them, it’s Wall Street that gets their way. It’s the world’s TBTF banks (they gave themselves that label) that get to call the shots on who lives in Greece and who does not. And they will never ever allow for any meaningful debt restructuring to take place. Which means they also call the shots on who lives in Berlin and New York and Tokyo and who does not. Did I mention Beijing, Shanghai, LA, Paris and your town?
Greece’s problem can only be truly solved if large scale debt restructuring is accepted and executed. But that would initiate a chain of events that would bring down the bloated zombie that is Wall Street. And it just so happens that this zombie rules the planet.
We are all addicted to the zombie. It allows us to fool ourselves into thinking we are doing well – well, sort of -, but the longer term implications of that behavior will be devastating. We’re all going to be Greece, that’s inevitable. It’s not some maybe thing. The only thing that keeps us from realizing that is that the big media outlets have become part of the same industry that Wall Street, and the governments it controls, have full control over.
And that in turn says something about the importance of what Yanis Varoufakis and Syriza are trying to accomplish. They’re taking the battle to the finance empire. And it should not be a lonely fight. Because if the international Wall Street banks succeed in Greece, some theater eerily uncomfortably near you will be next. That is cast in stone.
As for the title, it’s obviously Marquez, and what better link is there than Wall Street and cholera?
No comments:
Post a Comment